Introduction

Whether or not drugs are criminalized in countries and municipalities, has a significant impact on communities, individuals, and more largely the healthcare system and prison system. Countries with two very different drug policies are Portugal and the United States. Portugal, in 2001, abolished all penalties for personal possession of drugs including, methamphetamine, marijuana, cocaine, and heroin (Greenwald, 2009). In contrast, the United States criminalizes personal possession for most illicit drugs, with the exception of marijuana in some states. Those states in the U.S. who decriminalized marijuana and Portugal both only allow small amounts to be possessed, but the distribution, sale, and transportation of drugs still remains illegal.
Portugal
About 19 years ago Portugal decriminalized the possession of all drugs, including cocaine and heroin. They believe that addicts fear the possibility of prison, therefore it drives them underground. Because incarceration is so expensive, Portugal decided to provide addicts with health services instead of prison time. Now under the Portuguese government, individuals found guilty of possession of small amounts of drugs are sent to psychologists, social workers and legal advisors to seek appropriate treatment (Szalavitz, 2009). By sending them to health workers instead of prison it allows them to “exercise complete responsibility for what he does and what happens to him “(Becker, 1973). In other words, it allows the individual to take control over their life, and change for the better instead of going in and out of jail and or prison. This has dramatically changed social institutions such has the healthcare system and the penal system.

Since the decriminalization of drugs, drug-related HIV cases dropped 75 percent. In addition, in 2002, 49 percent of people with AIDs were addicts, but in 2008 the number dropped to only 28 percent (Szalavitz, 2009). Death by results of heroin in particular dropped by nearly more than half since the new regime. Although the cases of HIV caused by sharing dirty needles dropped, the number of people seeking help for their addiction doubled. The government was able to save a lot of money from the new enforcement and therefore was able to increase the funding for drug-free treatments (Szalavitz, 2009). This may be the case, but seeking help is much better than the alternatives, such as death and prison. For every million people in Portugal, only three people die as a result of overdose (Ingraham, 2015). This is dramatically different from other countries in Europe who report dozens, even hundreds, per million people dying of overdoses. The penal system has also significantly and positively been impacted by the new drug laws that were put in place over a decade ago. Between the years of 2000 and 2008, drug-related court cases dropped by 66 percent. All of the money that was once going towards the justice system has since been diverted to the public health service (Szalavitz, 2009). This has overall changed society in Portugal for the better.
The United States
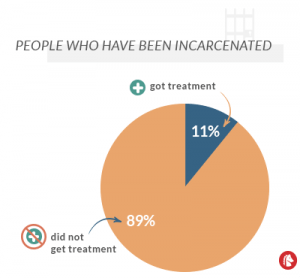
Illicit drug use remains illegal in the U.S. with the exception of some states in which decriminalized the possession of small amounts of marijuana. The numbers of people in prison as a result of drug possession and use are drastic. The United States only contains about 5 percent of the worlds population but 25 percent of their prisoners. Of all of the drug related arrests, narcotics compromise 12 to 28% of them (Thompson, 2017). Likewise, the U.S. has spends about $74 billion a year on criminal and court proceedings for drug offenders, compared to only $3.6 billion for drug treatment (Szalavitz, 2009). The United States should be more focused on treatment rather than sending addicts to prison. As of 2018, 15,000 people died of overdose due to heroin. This is at a rate of 5 deaths for every 100,000 Americans (Heroin Overdose Data, 2020). This is exceptionally higher than the rate of deaths as a result of overdose in the country of Portugal. If all illicit drugs, not just marijuana, were to be decriminalized, both the penal system and healthcare system would change, and probably for the better. Not only would the recidivism rate go down, but so would the death rate as well as the rate of HIV diagnosis.
Conclusion
Many countries have different laws and regulations pertaining to drugs. Above I looked at two countries, Portugal and the United States. Portugals drug policy is very lenient with the decriminalization of all drugs, including cocaine and heroin. They are more focused on helping addicted individuals and providing them treatment rather than throwing them in prison. The U.S, on the other hand, only decriminalized marijuana in some states, still obtaining their law against the legalization of other illicit drugs. They are more focused on putting drug offenders in prison rather than getting them the help that they need. They are slowly transitioning to more treatment opportunities and moving away from harsh sentences for drug users.
References
Becker, Howard S. Outsiders Studies in the Sociology of Deviance. 1973.
Greenwald, G. (2009). Drug Decriminalization in Portugal: Lessons for Creating Fair and Successful Drug Policies. SSRN Electronic Journal. doi: 10.2139/ssrn.1543991
Heroin Overdose Data. (2020, March 19). Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/drugoverdose/data/heroin.html
Ingraham, C. (2015, June 7). The EU country where drugs are decriminalised – and hardly anyone dies of an overdose. Retrieved from https://www.independent.co.uk/news/world/europe/portugal-decriminalised-drugs-14-years-ago-and-now-hardly-anyone-dies-from-overdosing-10301780.html
Szalavitz, M. (2009, April 26). Drugs in Portugal: Did Decriminalization Work? TIME.
Thompson, B. Y. (2017). “Good moral characters”: how drug felons are impacted under state marijuana legalization laws. Contemporary Justice Review, 20(2), 211–226. doi: 10.1080/10282580.2017.1307109